- Know
how States in India & U.S. came into being. Were they reorganised,
purchased or conquered? Why were Linguistic States made? What is the concept of
Cultural Unity & Nationhood in India? Differences between Indian and U.S.
states?
Some
learned believe that India is a federation of states like the U.S. Rahul Gandhi said, “India is described in the Indian Constitution as a union
of states and not as a nation. One cannot rule over the people of a state in
India. Different languages and cultures cannot be suppressed.” To hear Rahul
speech in Parliament Click
Keep
politics aside. Is India a union of states or
federation and a Nation?
It
is worth recalling what Ambedkar said, “India is a single geographical unit.
Her unity is as ancient as Nature. This cultural unity has defied political and
racial divisions.” Pg. 29 A New Idea of
India Further, India is integrated by Visible, Distinct and Recognisable
Binding Common Threads of Indic Civilizational and Cultural Nationhood.
Pilgrimage
is a form of cultural unity. Therefore, this devotee from Rajasthan visited
Rameshwaram in Tamil Nadu.
 Elderly man from Rajasthan in Rameshwaram. Pic 2016.
Elderly man from Rajasthan in Rameshwaram. Pic 2016.
So
also Indians from all over visit Kamakya Mandir in Guwahati, Assam.
 Devotees from Andhra Pradesh in Guwahati. Pic 2013.
Devotees from Andhra Pradesh in Guwahati. Pic 2013.
Columnist Sandhya Jain explained the
concept of cultural unity and nationhood in Daily
Pioneer, “Pranabda (former
President) punched a hole in the Westphalian model of nationhood, asserting
that India was a state long before the European Nation State rose after 1648,
based on the notion of a defined territory, single language, shared religion
and a common enemy. We may highlight here the difference between Indian and
Western notions of ‘universal’. The Hindu meaning is that which is applicable
or can be adopted voluntarily by all (e.g. Yoga, mutual coexistence without
strife, etc.). The monotheist concept is that which should be imposed upon all
(religion, culture, thinking, et al).”
Also
read Culture
is the root of Indian Nationhood
Actually, Indian
culture exists across modern day borders. Thus, India welcomes to Bodh Gaya, devotees
from Southeast Asia just like Mount Kailash Yatra in Tibet attracts Indian
devotees.
 Devotees from Burma in Bodh Gaya, Bihar. Pic 2012.
Devotees from Burma in Bodh Gaya, Bihar. Pic 2012.
 Devotees from Nepal at Rameshwaram. Pic 2016.
Devotees from Nepal at Rameshwaram. Pic 2016.
So also Indian culture went to different
places for e.g. Xinjiang, China.
 Shiva
and Parvati, Mural, Kizil Caves, Kucha, Xinjiang, 6th Century. Pic by Benoy K
Behl
Shiva
and Parvati, Mural, Kizil Caves, Kucha, Xinjiang, 6th Century. Pic by Benoy K
Behl
To understand the difference between Union of States and a
Federation i.e. U.S. one needs to know how the countries got their present form. Let us start with India.
When
British ruled there were areas administered by the British and Rulers for e.g.
Baroda, Mysore, Udaipur and Travancore. In 1947 India was formed by merger of
all the princely states and those areas directly under British rule e.g. Bombay
Presidency.
So which were states during British rule and what happened
post-Independence?
Burma
became a part of India as an administrative in 1836. The Government of India
Act 1935 separated Burma from India and created the provinces of Orissa, Sindh.
2 Pg. 543. Originally, Orissa was
part of Calcutta Presidency and Sindh of Bombay.
Till
1905 Bengal included Bihar and Orissa and Assam, in full or part. The princely state of Cooch
Behar was included in the political map of Bengal after Independence. Earlier,
the northern region of Bengal was ruled by the Koch Dynasty. Source “A separate province of Assam (administered by a chief
commissioner) was created in 1874 with its capital at Shillong.
In 1905 Bengal was partitioned into West and East. Assam was
amalgamated with East Bengal; this created such resentment, however, that in
1912 Bengal was reunited, and Assam was once more made a separate province.” Source
Bihar
and Orissa were separated from Bengal Presidency to form new provinces in 1912.
In 1936 Orissa got separated from Bihar. Source
Princely states of Orissa got merged into it post-independence.
In
India the area covered was one. Changes were made for administrative
convenience amongst others. This did not involve adding new areas except Cooch
Behar that was anyway part of India-The Cultural Unit.
From
Assam smaller states were carved out for different reasons. Nagaland in 1963,
Manipur, Tripura and Meghalaya in 1972 and Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh in 1987. Source Sikkim became a state in 1975. Read Tripura
Instrument of Accession
Coming to the West. Areas under Bombay Presidency were Sindh, Gujarat, Western Maharashtra and a number of princely states where indirect rule applied. Source
Sindh
became a separate province in 1936. After Independence, Bombay Presidency
became Bombay State which was split into Gujarat and Maharashtra in 1960. The
Samyukta Movement ensured that Bombay remained with Maharashtra. The new
capital of Gujarat was Gandhinagar. Since
Bombay (now Mumbai) was the commercial capital large number of Gujaratis
settled in Bombay.
The
newly created states in the West were part of India-The Cultural Unit and did
not involve buying or conquering new areas.
Next
South. “The Madras Presidency, during the
British, covered a vast expanse of the southern part of India that encompasses
modern-day Tamil Nadu, the Lakshadweep Islands, Northern Kerala, Rayalaseema (Andhra
Pradesh), Coastal Andhra, districts of Karnataka and various districts of
southern Odisha.” Source
Freedom
fighter Potti Sreeramulu’s 56 day hunger-strike and death to draw attention to
demand for a state of Telegu speaking regions of Madras resulted in the
formation of Andhra Pradesh in 1953. Note Hyderabad became part of India in
1948.
Eventually, a States Reorganization Commission
was formed in 1955 and the States
Reorganisation Act (SRA) passed in 1956.
The state of Kerala was formed in 1956 when, “Travancore-Cochin state was merged with Malabar district of
Madras and Kasaragod taluk of South Canara district. Parts of Southern
Travancore-Cochin on the other hand went to Madras state.” Source
In
1956 Madras was divided further, with some areas going to the new state of
Kerala and other areas becoming part of Mysore. What remained of Madras
state was renamed Tamil Nadu in 1968.” Source
Mysore was renamed as Karnataka in 1973.
Back to North.
Punjab in 1947 consisted of modern day Punjab, Himachal Pradesh and Haryana.
Dogra Kings ruled over Jammu and Kashmir. The linguistic state of Punjab was
created in 1966. Himachal became a Union Territory first and then a State in
1971.
Also read Merger
of Princely States into Punjab, Language controversy
Uttar Pradesh got its name around 1949. The province was
called United Province of Agra and Oudh since 1902. It was changed to United
Province in 1937. Source Uttarakhand was carved out of U.P. in 2000.
Madhya Pradesh got its name in
1956. MP was earlier divided into several small kingdoms which were captured by
the British and incorporated into Central provinces and Berar and the Central
India Agency by early 18th century. Source
“The
Central Provinces was formed in 1861 by the merger of the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories and Nagpur Province. Administration of the Berar region of the Hyderabad princely state was
assigned to the Chief Commissioner of the Central Provinces in
1903, and for administrative purposes, Berar was merged with the Central
Provinces to form the Central Provinces & Berar on 24 October 1936.” Source
In
1913 it was known as the Central Provinces Legislative Council. After
Independence a number of princely states merged with the earlier Central
Provinces and Berar to form Madhya Pradesh. Bhopal State (ruled by the Nawab),
merged with India in 1949.
“After
independence, MP state was created with Nagpur as its capital: this state
included the southern parts of the present-day Madhya Pradesh and north-eastern
portion of today’s Maharashtra. In 1956, the state was reorganised by excluding
the Maratha speaking areas (that became part of Bombay State) and its parts
were combined with the states of Madhya Bharat, Vindhya Pradesh and Bhopal to
form the new MP state with Bhopal as its capital.” Source
and Source
Chhattisgarh was carved out of MP in 2000.
 Devotees from Thailand in Pushkar, Rajasthan.
Devotees from Thailand in Pushkar, Rajasthan.
This organization and re-organization met regional
aspirations by creating linguistic states and making bigger states smaller.
These states have allowed regional languages to blossom.
How were Linguistic States born?
The seeds were sown when the Nagpur
Congress of 1920 accepted linguistic provinces. Thus, were created provincial
Congress Committees by linguistic zones.
Also read Linguistic
Provinces are the foundation of India’s Federalism and Unity And Formation
of Linguistic States
Some think that linguistic states would weaken
India.
Freedom-fighter,
historian and founder of Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan Dr K M Munshi wrote in Foreword
to Volume 11, “In India the greatest danger is the formation of sub-nation
States and linguistic chauvinism. Formation of states based on language was an
administrative necessity and after Independence some adjustments were made but
it was impossible to draw the boundaries of a state in such a manner as to
totally exclude linguistic groups from the adjacent States. Nor is such a
boundary necessary. We are citizens of India, not of any State, though the
present trend is to identify oneself with his State rather than India.”
“This
tendency has to be dealt with firmly without weakening the Centre or the
federal bonds in any way. It has been the experience of history, that this
subcontinent has fallen a prey to foreign invasion in the absence of a strong
central authority. This lesson of history we had in mind when we adopted a
quasi-federal constitution of India.” 1
What did Ambedkar say about
India being a Union of States?
Article
1 of the Constitution states, “India i.e. Bharat, shall be a Union of States.”
Narayan Ramachandran quoted
Ambedkar in the MINT, “the use of the term ‘Union’ is deliberate. The Drafting Committee wanted to make it clear that though India was to be a federation, the federation was not the result of an agreement by the states to join a federation and that the federation not being the result of an agreement, no state has the right to secede from it. It also explains the fact that the Union is indestructible but not the States; their identity can be altered or even obliterated."
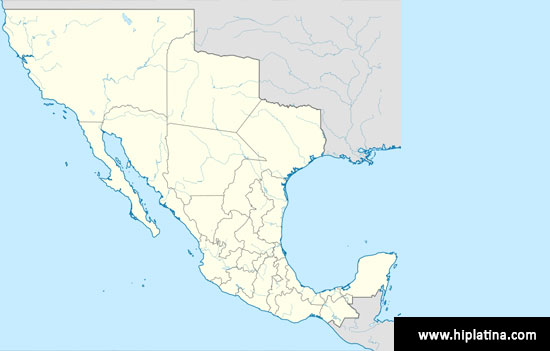 Ten U.S. states that were once part of Mexico.
Ten U.S. states that were once part of Mexico.
Now how did the U.S. become the United States of America?
1. The United States emerged from
the Thirteen British Colonies established along the East Coast. Disputes with Great Britain representation led to the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), which established the nation's independence. Source Land
acquired from France by the Louisiana Purchase (1803)
nearly doubled the country’s territory.
2. U.S. bought
Florida east and west from Spain, annexed Texas in 1845, acquired Oregon
Territory from Britain in 1846, Mexican
Cession purchased from Mexico following military victory in 1848, Gadsden
purchased from Mexico in 1853, Alaska purchased from Russia
in 1867, Annexation of Hawaiian Islands in 1898 and Midway Islands in 1867 and
so on. Source
Also read Annexation
of Texas And Annexation of
Hawai 1898
3. 10 U.S. States
that were once part of Mexcio Source
California
was under Mexican rule from 1821, when Mexico gained its independence from
Spain, until 1848. Nevada and New Mexico are states that was once under Mexican
control. Arizona came under U.S. control in 1848 and didn’t become a state
until 1912. Before 1848, Arizona was part of the Mexican state of Sonora. Texas
was part of Mexico, from 1821 to 1836. Read more Here
Also, “Puerto Rico was
a Spanish colony until 1898, when the U.S. gained control of it, as part of the
terms ending the Spanish-American War. Puerto Rico is one of 5 inhabited U.S.
territories where People are U.S. citizens, pay federal taxes such as Social
Security and Medicare – but not federal income tax. To
read more and Source
India
did acquire miniscule areas from Portugal and France. These were either merged
with neighbouring states or given status of union territories. Goa became a state in 1987. However, they were
part of India Cultural Unit before conquest.
It
is not my intent to evaluate the circumstances under which these states became
part of the U.S. The nature of any Constitution is a consequence of the
historical moment when drafted.
The
point being made is that unlike India which was always one geographical and
cultural unit, U.S.A. increased its land mass through war, purchase, agreements
etc. Indian states were re-organised to meet regional aspirations and for
administrative purposes. India had cultural unity for centuries.
Also read Medical
geography of India in Charaka Samhita
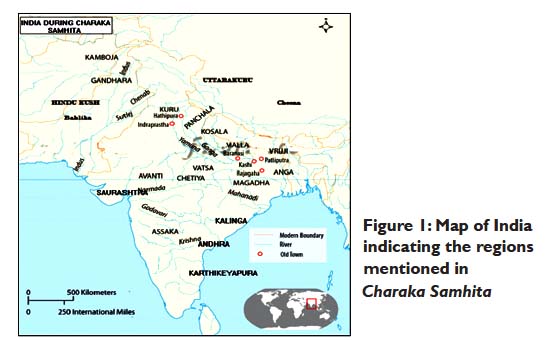 Map in Charaka Samhita. Credit AYU Journal, Oct-Dec 2014 issue.
Map in Charaka Samhita. Credit AYU Journal, Oct-Dec 2014 issue.
A few key differences between U.S. and Indian States
In
the U.S. every state has its own flag
unlike India.
A
Governor in the U.S. is “chief officer in their
state. They function as the head of State government, therefore overseeing the
proper functioning of the state. Additionally,
many governors have significant influence over the legislature and judiciary,
being able to veto state bills, appoint judges and in some states having either
some or complete control over the ability to pardon a criminal sentence.” Most
have terms of four years. Governors are elected as also the attorney generals. Source
In
India the Governor is appointed by the President, does not have a fixed term
and the powers as in the U.S. It is a titular post. Read Constitutional and Statutory
Duties of the Governor of Texas
Each
U.S. state has its own written constitution unlike India that has one
constitution. Source
Powers not granted to the Federal government are reserved for
States in the U.S. Source
unlike India where there is State, Union and Concurrent List.
Concluding, author-lawyer J Sai Deepak wrote, “Bharat
civilization may be understood as a federal civilization with multiple
sub-identities that are free to retain their identities but have remained
culturally and politically bound for millennia.” 2 Pg. 185. Each state in the
Union shall have the right to have its own regional language as its state
language.
Just
like every soul, every country is different. Whilst comparing India with other
countries keep in mind that its culture, thought and evolution are unique.
Also read Comparing
Indic faiths vs Abrahamic religions-A Primer
Author
does not claim to know it all. In case of any errors, please email edits with
source document reference, shall change.
References
1.
The History and Culture of Indian People
2.
India that is Bharat by J. Sai Deepak
3. 26
districts of Madras Presidency
Also read
1. Names
of Buddhist sites in Xinjiang-Sanskrit on the Silk Route
2. Scholar
Pilgrims from India to China
3. Kailash
Mansarovar Yatra is eternal
4. Ramayana
in Southeast Asia
5. Samskriti,
Sanskrit and Indonesia
6. Hindu
Deities in Japan
7. Federalism
Forms in India – informative
8. Union, State and Concurrent
Lists
9. Formation
of New States